|
For EC&M Magazine
By Mike Holt, NEC® Consultant
Here's the follow-up to yesterday's newsletter.
This includes the answers to the questions sent, so you can see how you did.
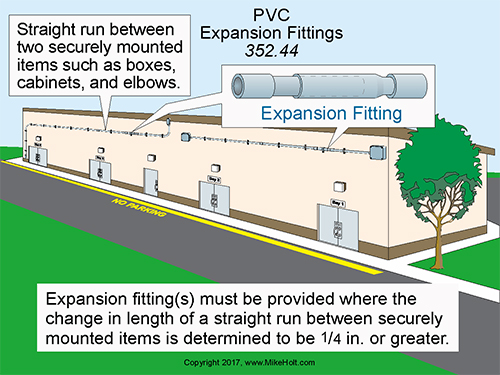
Figure 01
|
 |
|
Figure 01
|
For EC&M Magazine
By Mike Holt, NEC® Consultant
Here's the follow-up to yesterday's newsletter.
This includes the answers to the questions sent, so you can see how you did.
Note: The answers to these questions are based on the 2017 NEC.
Q1. What is the NEC requirement for securing and supporting PVC conduit?
A1. PVC conduit must be fastened and supported in accordance with 352.30(A) and (B) so movement from thermal expansion and contraction is permitted.
Secured. PVC conduit must be secured within 3 ft of every box, cabinet, or termination fitting, such as a conduit body [352.30(A)].
Supports. PVC conduit must be supported at intervals not exceeding the values in Table 352.30, and the raceway must be fastened in a manner that permits movement from thermal expansion or contraction [352.30(B)].
Table 352.30 |
Trade Size |
Support Spacing |
½“1 |
3 ft |
1¼“2 |
5 ft |
2½“3 |
6 ft |
3½“5 |
7 ft |
6 |
8 ft |
PVC conduit installed horizontally in bored or punched holes in wood or metal framing members, or notches in wooden members, is considered supported, but the raceway must be secured within 3 ft of termination.
Q2. What are the Code requirements for expansion fittings in PVC conduit runs?
A2. If PVC conduit is installed in a straight run between securely mounted items, such as boxes, cabinets, elbows, or other conduit terminations, expansion fittings must be provided if the expansion or contraction length change, in accordance with Table 352.44 is expected to be ¼ in. or greater [352.44]. Figure 01
Table 352.44 Expansion Characteristics of PVC Rigid Nonmetallic Conduit Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
Temperature Change (ºC) |
Length of Change of PVC Conduit (mm/m) |
Temperature Change (ºF) |
Length Change of PVC Conduit (in./100 ft) |
5 |
0.30 |
5 |
0.20 |
10 |
0.61 |
10 |
0.41 |
15 |
0.91 |
15 |
0.61 |
20 |
1.22 |
20 |
0.81 |
25 |
1.52 |
25 |
1.01 |
30 |
1.83 |
30 |
1.22 |
35 |
2.13 |
35 |
1.42 |
40 |
2.43 |
40 |
1.62 |
45 |
2.74 |
45 |
1.83 |
50 |
3.04 |
50 |
2.03 |
55 |
3.35 |
55 |
2.23 |
60 |
3.65 |
60 |
2.43 |
65 |
3.95 |
65 |
2.64 |
70 |
4.26 |
70 |
2.84 |
75 |
4.56 |
75 |
3.04 |
80 |
4.87 |
80 |
3.24 |
85 |
5.17 |
85 |
3.45 |
90 |
5.48 |
90 |
3.65 |
95 |
5.78 |
95 |
3.85 |
100 |
6.08 |
100 |
4.06 |
Author's Comment:
• When determining the number and setting of expansion fittings, you must be sure to actually read the manufacturer's documentation. For example, instructions for Carlon® expansion fittings for PVC states that when the PVC has sunlight exposure, we must add 30ºF to the high ambient temperature.
Q3. What is the NEC rule for the installation of bushings on PVC conduit terminations?
A3. Where PVC enters a box, fitting, or other enclosure, conductors 4 AWG and larger must be protected from abrasion, during and after installation, by a fitting that provides a smooth, rounded insulating surface [300.4(G)] [352.46].
Informational Note: Conductors 4 AWG and larger that enter an enclosure must be protected from abrasion, during and after installation, by a fitting that provides a smooth, rounded insulating surface, such as an insulating bushing, unless the design of the box, fitting, or enclosure provides equivalent protection, in accordance with 300.4(G).
Author's Comment:
• When PVC conduit is stubbed into an open-bottom switchboard, the raceway, including the end fitting (bell-end), must not rise more than 3 in. above the bottom of the switchboard enclosure [300.16(B) and 408.5].
Q4. What uses are permitted by the Code for Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit?
A4. Listed liquidtight flexible nonmetallic conduit is permitted, either exposed or concealed, at any of the following locations [356.10]:
Informational Note: Extreme cold can cause nonmetallic conduits to become brittle and more susceptible to damage from physical contact.
(1) If flexibility is required.
(2) If protection from liquids, vapors, or solids is required.
(3) Outdoors, if listed and marked for this purpose.
(4) Directly buried in the earth, if listed and marked for this purpose.
(5) LFNC (gray color) is permitted in lengths over 6 ft if secured in accordance with 356.30.
(6) LFNC, Type B (black color) as a listed manufactured prewired assembly.
(7) Encasement in concrete if listed for direct burial.
Q5. What uses are not permitted by the NEC for Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetalic Conduit?
A5. Liquidtight flexible nonmetallic conduit cannot be used if:
(1) subject to physical damage [356.12].
(2) the ambient temperature and/or conductor temperature is in excess of its listing.
(3) Longer than 6 ft, except if approved by the authority having jurisdiction as essential for a required degree of flexibility.
(4) In any hazardous location, except as permitted by 501.10(B), 502.10(A) and (B), and 504.20.
Author's Comment:
• Liquidtight flexible nonmetallic conduit, (LFNC), is more or less a flexible version of PVC and is actually made from a more pliable type of PVC more commonly referred to as Carflex®.
|

